4 December 2019
for Madrid Nuevo Norte
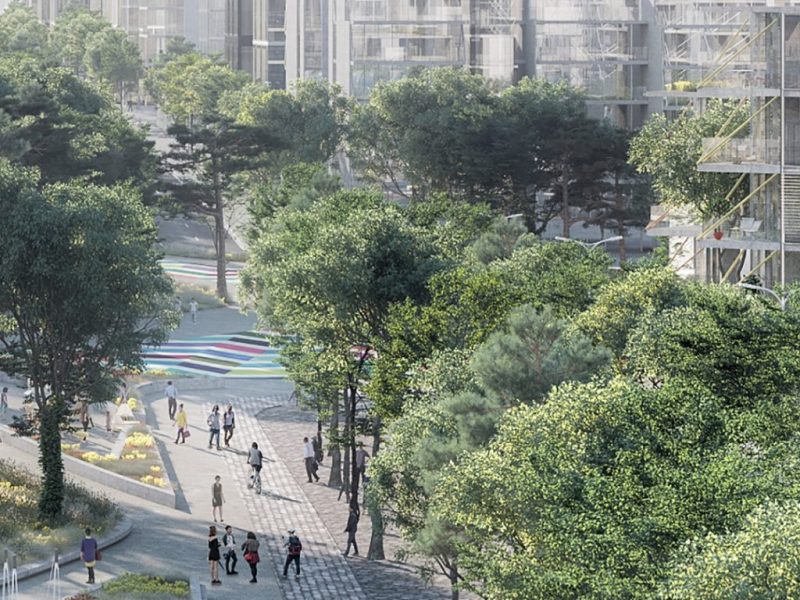

The urban infrastructures of Madrid Nuevo Norte, which were presented at the United Nations Climate Summit (COP25), meet the need to transform cities into opportunities to fight against climate change

Nuevo Norte’s sustainability strategy has been discussed at the United Nations Climate Summit (COP25). This major urban regeneration project in Madrid seeks to become a benchmark for urban sustainability and innovation and looks forward to scaling up the measures applied to the regional, national and international levels. Hence, Distrito Castellana Norte was invited to several forums of this critical summit to expound on Madrid Nuevo Norte’s proposal on how to face the challenges of future cities. One of the issues tackled in this summit was the role that Madrid Nuevo Norte’s urban infrastructures play as a tool for fighting climate change.
Madrid Nuevo Norte stems from the comprehensive renovation of Chamartín Train Station that seeks to close the gap that divides into two the capital’s northern districts. The project is committed to a compact, dense, city model with mixed uses that seeks to create living public spaces. Indeed, from the outset, it was geared towards sustainable mobility. Its urban infrastructure was designed to enhance the environmental values and well-being of individuals, and ensure sustainable mobility and efficient use of energy during the urban planning and building process. All this builds on smart infrastructure management systems, which will enable real-time adaptation of transport infrastructures to specific needs arising at any given time.
Sustainable mobility has played a key role in Madrid Nuevo Norte since the early stages of the design phase. The project leverages the vast potential of Chamartín Train Station to minimise commuting and build an extensive public transport network to encourage intermodal transport, walking and cycling to reach a target of 80% of commutes by public transport.
Madrid Nuevo Norte’s mobility proposal also includes several pioneering initiatives that are a first in our environment, including restyling intermodal transport hubs into centres of urban life or gradual restructuring of parking spaces for alternative uses, such as proximity logistics, among others. The project is a forerunner of new social and economic trends, including new forms of “last mile” urban logistics, i.e. freight and parcel delivery. It will also lay the grounds for infrastructure needed for substantially increasing the use of shared, standalone, electric mobility.
Madrid Nuevo Norte envisages environmental values as an integral element of the urban fabric. It not only preserves and respects current environmental values but also seeks to create its own ecosystem for promoting biodiversity. To that end, it leverages its prime location, next to Cuenca Alta del Manzanares Regional Park and El Pardo Forest, to connect the urban centre of Madrid with nature.
These approaches have resulted in various infrastructures, including the 3-km long green corridor that will connect the project with El Pardo Forest, and new ecological connection structures between the pre-existing urban parks in nearby neighbourhoods and Madrid Nuevo Norte. The current void of the rail tracks near Chamartín Station will be replaced by a large central park that will be built on one of the largest decks of its kind at the international level.
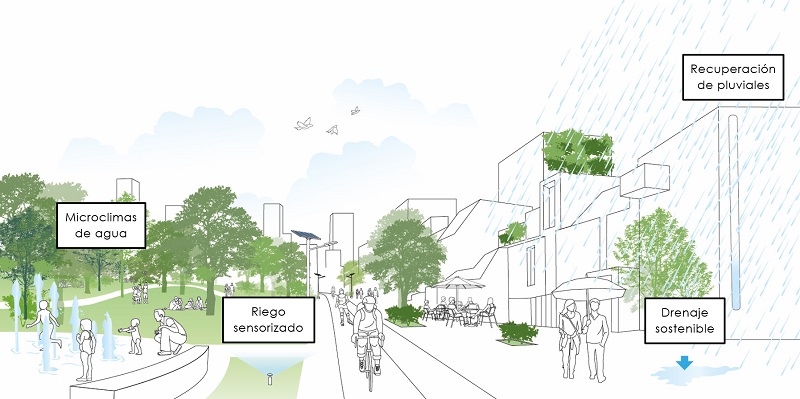
These environmental measures are complemented by a strategy to mitigate the heat-island effect and a microclimate study to ensure the comfort of people.
Efficient use of resources is another major cornerstone to ensure infrastructure sustainability, both in terms of construction and urbanisation, as well as during the project operation phase. To that end, energy decarbonisation through electrification, energy efficiency, renewable energy production and smart systems will be a crucial factor. Madrid Nuevo Norte aims to increase renewable energy production to double the amount required by future building regulations.
Additional pioneering measures in our geographical setting are also planned, including the introduction of heating networks for district heating and cooling, as well as power distribution networks, consisting of multiple, small-scale, power generation systems installed near the consumer. These initiatives seek to make Madrid Nuevo Norte a zero-emission district.
Madrid Nuevo Norte also aims to become a benchmark for sustainable management of water resources, linking urban infrastructures with the water cycle, planning efficient and sustainable use of water, and maximising self-sufficiency with water catchment, savings and efficiency-related initiatives. These measures include seeking the maximum permeability of the street surface and reusing rainwater for watering green areas.
As for materials used, Madrid Nuevo Norte applies a comprehensive approach to the building materials cycle and incorporates circular economy principles to ensure a low carbon footprint through the selection of appropriate materials, management of construction and demolition waste, recycling, reuse of materials and on-site prefabrication to minimise the impact of the works on the urban environment.